‘SMMR-Explore: SubMap-based Multi-Robot Exploration System with Multi-robot Multi-target Potential Field Exploration Method’ Paper Review
‘SMMR-Explore: SubMap-based Multi-Robot Exploration System with Multi-robot Multi-target Potential Field Exploration Method’ 논문 리뷰 포스팅입니다.(작업 중)
0. Reference
J. Yu et al., “SMMR-Explore: SubMap-based Multi-Robot Exploration System with Multi-robot Multi-target Potential Field Exploration Method,” 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2021, pp. 8779-8785, doi: 10.1109/ICRA48506.2021.9561328.
1. Introduction
미지 영역을 탐사하는 것은 autonomous robot system에서 근본적인(가장 중요한) 일이다.
전형적인 탐사는 두 가지 파트로 이루어져 있는데 이는 인식&위치(perception & location)와 결정(decision)이다.
Perception & Location의 경우, DSLAM(Distributed SLAM)이 서로 다른 로봇이 동일한 장소를 경험할 때 로봇 간의 상대적 자세를 제공한다.
Decision의 경우, 로봇은 같은 장소를 경험하기 전 개별적으로 환경을 탐색하고, 상대적인 자세가 제공되면 협력적으로 탐색을 진행한다.
Multi robot exploration task에서 지도는 필수불가결하다.
그러므로 지도는 로봇 간 항상 공유된다.
지도는 암묵적으로 센서와 장면에 대한 정보를 포함하므로, 지도 자체만으로 place descriptor와 센서 데이터에 대한 중복 통신 없이, Place Recognition과 Relative Pose Estimation에 사용될 수 있다.
Frontier-based exploration방법은 단일 혹은 멀티 로봇 탐사에서 넓게 사용되어지고 있다.
로봇들은 우선적으로 현재 지도에 기반하여 Known과 Unknown 영역의 사이(also known as frontiers)의 나눠진 점들을 감지한다.
그리고 각 로봇은 information gain, travel cost, 그리고 다른 요소들을 고려한 detected frontier들을 통해 다음 목표를 지정한다.
현재 Sample-based 탐사 방법은 낮은 계산량 혹은 계산 시간으로 인해 최첨단이다.(state-of-the-art)
하지만 이런 방법의 탐색의 효율성은 두 가지의 근본적인 결함으로 인해 궤도 중첩과 small passage(좁은 통로)에서 downgrade를 겪는다.
두 가지의 근본적인 결함 :
- 새로운 sampled frontier는 다른 frontier cluster 사이에서 목표 지점 점프를 발생시킨다.
- map에 커짐에 따라 map points의 개수에 따른 frontier의 개수의 비율이 줄어든다.
대체적으로, 지도의 sampled 정보만 이용하는 것은 비난받아야한다.(?)
따라서, 더 많은 계산 자원의 희생 없이 frontier를 감지하고 선택하기 위해 완전한 지도 정보를 활용할 수 있는 새로운 탐색 패러다임이 요구된다.
본 논문의 제안 방식:
- Fully submap-based DSLAM Method. submap에 기반한 Place Recognition과 Relative Pose를 로봇간 공유한다.(30%의 데이터 중복 통신을 제거한다.)
- Multi-Robot Multi-target Potential Field (MMPF) exploration method. MMPF는 Frontier의 완전한 정보를 활용하여 최적의 Frontier 목표를 선정함으로써 궤적 중복을 제거하고 탐사 효율을 높인다.
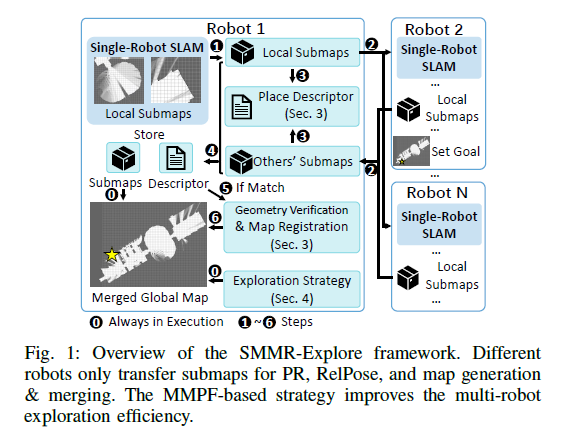
- Cartographer이용 단일 로봇이 submap을 구축.
- submap을 연결하면 단일 로봇 맵이 생성되고, 주어진 relative pose를 통해 로봇 간 맵이 병합된다.
- 각 submap은 로봇 간 공유되며, NN-Based 방법은 각 submap을 feature vector로 인코딩하여 로봇 간 loop closure를 감지하기 위해 추가 매칭을 수행한다.
- MMPF 기반 탐색 방법은 own-single robot map 혹은 merged global map을 통해 로봇을 guide한다.
2. Related Work
A. DSLAM System
centralized나 decentralized 방식과 같은 이전의 multi-robot SLAM 시스템은 두 가지의 기본적인 요소를 포함한다.
- Place Recognition
- Relative Pose Estimation
이 방법들은 모두 같은 장소를 찾아내기 위한 place descriptor를 계산한다.
하지만 센서나 방식에 따라 다른 유형의 데이터를 사용하는데,
image sensor 데이터를 이용하는 NetVLAD나 image feature point에 기반하는 Bag of Words나 3D laser sensor data를 이용하는 Segmatch 등이 있다.
Geometric Vertification (이미지 feature간 매칭과 같은 것)의 추정과 place descriptor의 two frame 간의 relative position을 최적화하는 것은 비슷하다.
3. Submap-Based DSLAM

위 Fig. 1.과 같이 DSLAM 시스템에서 로봇 간 데이터를 처리하는 데는 두 가지의 주요한 요소가 있다.
-
Place recognition and Matching (PR)
-
inter-robot relative pose estimation
로봇 간 상대 위치 추정
파트 3 에서는(현재 파트) 이 둘을 submap에 기반해 구현한다.
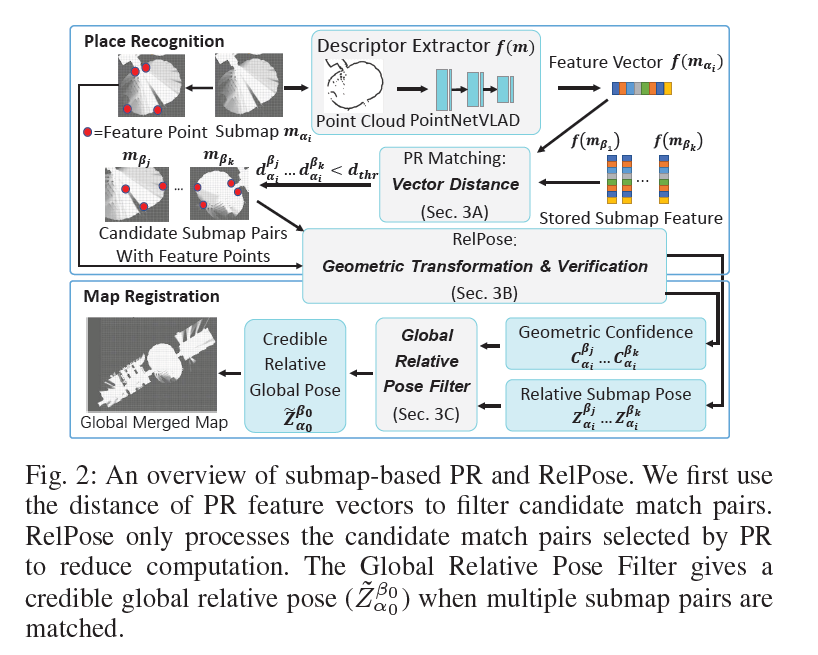
$ m_{\alpha_{i}} $는 robot $ \alpha $의 $i$번째 submap을 의미한다.
Place Recognition method는 같은 장소를 찾기 위해 $ m_{\alpha_{i}} $의 descriptor를 매치한다.
Relative Pose Estimation method는 $ m_{\alpha_{i}} $, $ m_{\beta_{j}} $ 두 submap 사이의 geometric confidence 인 $C_{\alpha_{i}}^{\beta_{j}}$ 와
geometric transformation인 $Z_{\alpha_{i}}^{\beta_{j}}$ 를 출력한다.

Leave a comment